Introduction
As the name suggests, the functionality averages the gray values of each pixel using the information of subsequent frames. This can be used to
- reduce the noise in an image and
- compensate motion in an image.
Balluff implemented a dynamic version of the frame averaging in the FPGA, which not need any CPU of the host system. However, this mode is only available for the
- BVS CA-GX2 (mvBlueCOUGAR-X2xx) cameras with larger FPGAs.
Dynamic mode of BVS CA-GX2 (mvBlueCOUGAR-X2xx)
This mode uses an adaptive recursive filter with an average slope. The slope sets the amount of new image versus averaged image in relation to the gray scale variation of the pixel. With it, static noise can be removed at full bit depth and full frame rate:
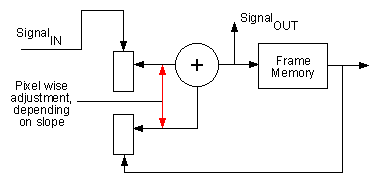
This method is well known and is used in the same or a similar way in all flat screen televisions. The amount of de-noising can be set with the slope factor: the smaller the value, the greater the feedback and therefore the de-noising but also the motion blur in the image:
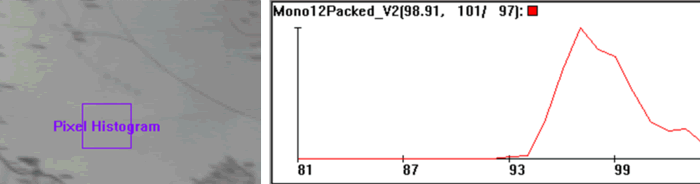
Slope: 256 = 100 % pixel_difference = 100 % signal_in
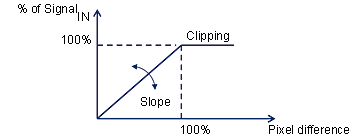
There are no delays with this option because de-noising is recursive and the SignalOUT is extracted before the frame memory.
Using ImpactControlCenter
Using the dynamic frame average mode, you have to do the following step:
- Start ImpactControlCenter and
- connect to the camera.
-
Then specify in "Setting → Base → Camera → GenICam → Device Control" which processing unit of the camera should do the frame averaging, e.g. unit 0 should do the frame averaging
"mv Device Processing Unit Selector = 0"
"mv Device Processing Unit = mvFrameAverage".
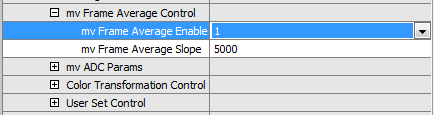
Afterwards, "mv Frame Average Control" is available. - Now open "Setting → Base → Camera → GenICam → mv Frame Average Control" and
- set the slope, e.g. 5000: "mv Frame Average Slope = 5000".
- Activate frame averaging by setting "mv Frame Average Enable = 1".
For "static images", setting average slope to small numbers (10 .. 1000) gives the best noise enhancement at the expense of motion blur.
For "dynamic images", setting average slope to higher values (1000 .. 5000) reduces motion blur at the expense of noise enhancement. This is especially needed in video application to enhance noise.