Installation¶
Warning
The instructions on Safety related to the rc_visard must be read and understood prior to installation.
The rc_visard offers a Gigabit Ethernet interface for connecting the device to a computer network. All communications to and from the device are performed via this interface. The rc_visard has an on-board computing resource that requires booting time after powering up the device.
Software license¶
Every rc_visard device ships with a pre-installed license file for licensing and protection of the installed software packages. The license is bound to that specific rc_visard device and cannot be used or transferred to other devices.
The functionality of the rc_visard can be enhanced anytime by upgrading the license, e.g., for optionally available software modules.
Note
The rc_visard requires to be rebooted whenever the installed licenses have changed.
Note
The license status can be retrieved via the rc_visard’s various interfaces such as the page of the Web GUI.
Power up¶
Note
Always fully connect and tighten the M12 power connector on the rc_visard before turning on the power supply.
After connecting the rc_visard to the power, the LED on the front of the device should immediately illuminate. During the device’s boot process, the LED will change color and will eventually turn green. This signals that all processes are up and running.
If the network is not plugged in or the network is not properly configured, then the LED will flash red every 5 seconds. In this case, the device’s network configuration should be verified. See LED colors for more information on the LED color codes.
Discovery of rc_visard devices¶
Balluff rc_visard devices that are powered up and connected to the local network or directly to a computer can be found using the standard GigE Vision® discovery mechanism.
Roboception offers the open-source tool rcdiscover-gui, which can be downloaded free of charge from
https://github.com/roboception/rcdiscover/releases for Windows and Linux.
The tool’s Windows version consists of a single executable for Windows 7, 10 and 11, which can be executed without installation.
For Linux an installation package is available for Ubuntu.
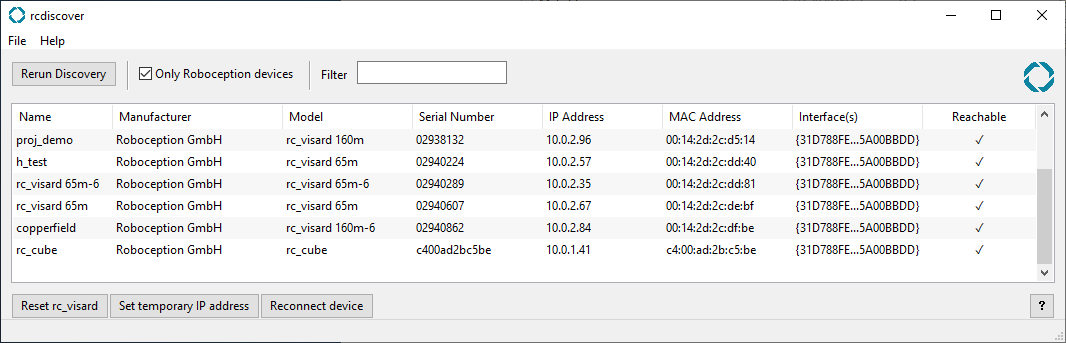
At startup, all available GigE Vision® devices – including rc_visard devices – are listed with their names, serial numbers, current IP addresses, and unique MAC addresses. The discovery tool finds all devices reachable by global broadcasts. Misconfigured devices that are located in different subnets than the application host may also be listed. A tickmark in the discovery tool indicates whether devices are actually reachable via a web browser.
After successful discovery, a double click on the device row opens the Web GUI of the device in the operating system’s default web browser. Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended as web browser.
Resetting configuration¶
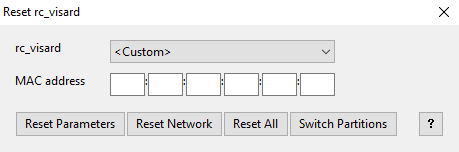
A misconfigured device can be reset by using the Reset rc_visard button in the discovery tool. The reset mechanism is only available for two minutes after device startup. Thus, the rc_visard may require rebooting before being able to reset the device.
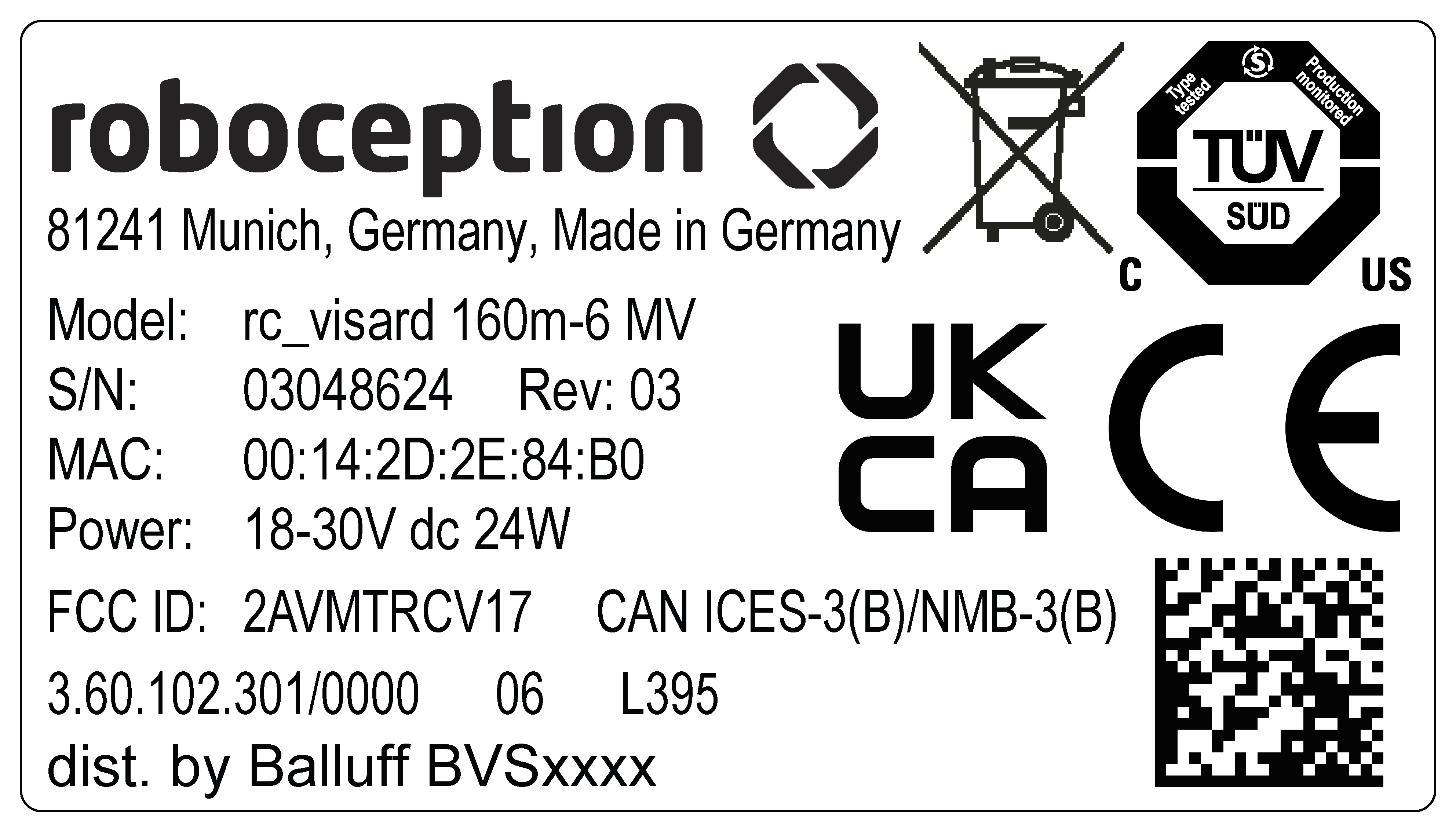
If the discovery tool still successfully detects the the misconfigured rc_visard, then the latter can be selected from the rc-visard drop-down menu. Otherwise, the rc_visard’s MAC address, which is printed on the device label, can be entered manually into the designated fields.
One of four options can be chosen after entering the MAC address:
- Reset Parameters: Reset all rc_visard parameters, such as frame rate, that are configurable via Web GUI.
- Reset Network: Reset network settings and user-defined name.
- Reset All: Reset the rc_visard parameters as well as network settings and user-defined name.
- Switch Partitions: Allows a rollback to be performed as described in Restoring the previous firmware version.
A white status LED followed by a device reboot indicates a successful reset. If no reaction is noticeable, the two minutes time slot may have elapsed, requiring another reboot.
Note
The reset mechanism is only available for the first two minutes after startup.
Network configuration¶
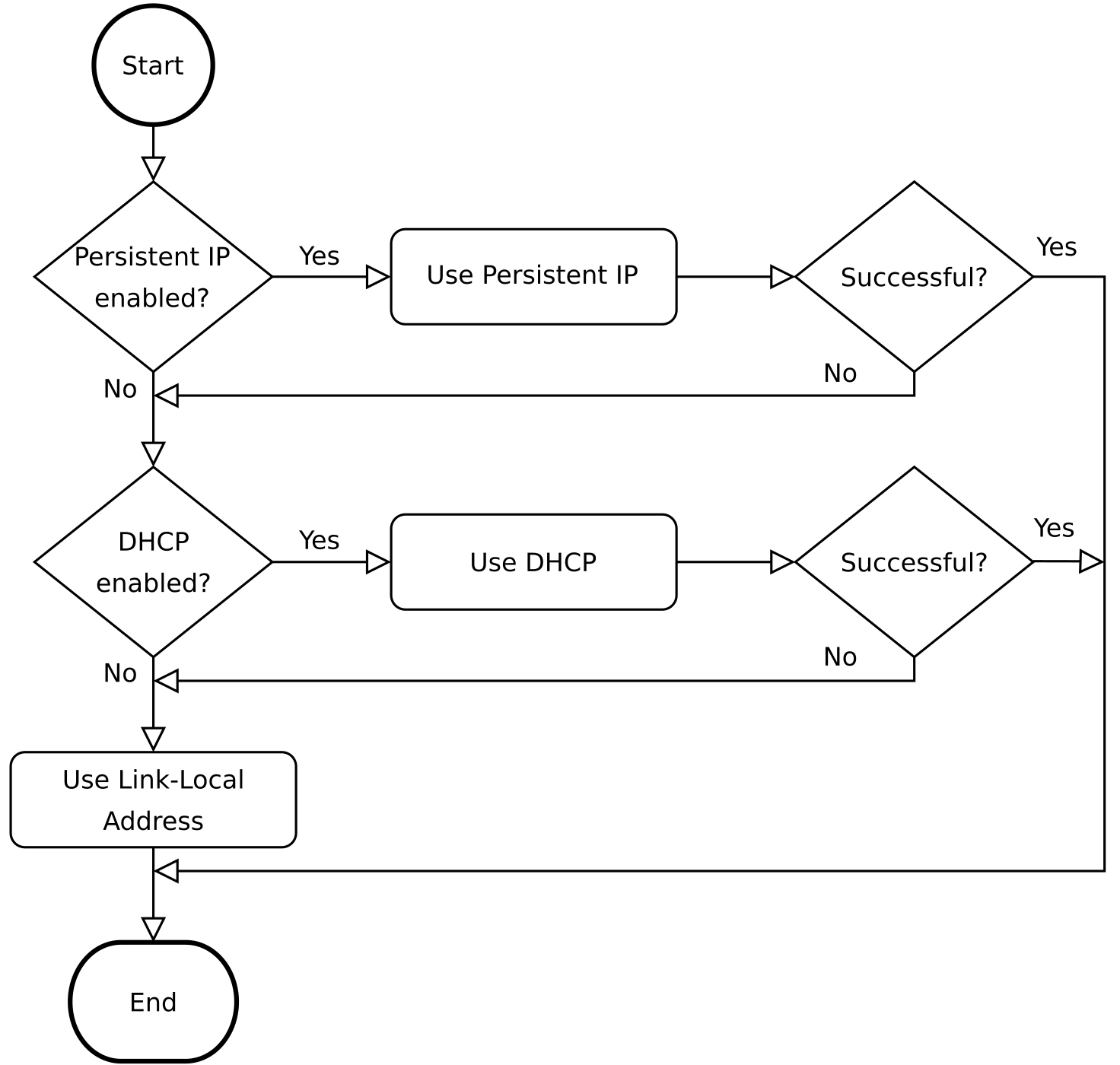
The rc_visard requires an Internet Protocol (IP) address for communication with other network devices. The IP address must be unique in the local network, and can be set either manually via a user-configurable persistent IP address, or automatically via DHCP. If none of these IP configuration methods apply, the rc_visard falls back to a Link-Local IP address.
Following the GigE Vision® standard, the priority of IP configuration methods on the rc_visard is
- Persistent IP (if enabled)
- DHCP (if enabled)
- Link-Local
Options for changing the rc_visard’s network settings and IP configuration are:
- the page of the rc_visard’s Web GUI – if it is reachable in the local network already, see Web GUI
- any configuration tool compatible with GigE Vision® 2.0, or Roboception’s command-line tool
gc_config. Typically, these tools scan for all available GigE Vision® devices on the network. All rc_visard devices can be uniquely identified by their serial number and MAC address, which are both printed on the device.- temporarily changing or completely resetting the rc_visard’s network configuration via Roboception’s
rcdiscover-guitool, see Discovery of rc_visard devices
Note
The command-line tool gc_config is part of Roboception’s open-source convenience layer rc_genicam_api,
which can be downloaded free of charge for Windows and Linux from http://www.roboception.com/download.
Host name¶
The rc_visard’s host name is based on its serial number, which is printed on the device, and
is defined as rc-visard-<serial number>.
Automatic configuration (factory default)¶
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is preferred for setting an IP address. If DHCP is active on the rc_visard, which is the factory default, the device tries to contact a DHCP server at startup and every time the network cable is being plugged in. If a DHCP server is available on the network, the IP address is automatically configured.
In some networks, the DHCP server is configured so that it only accepts known devices. In this case, the Media Access Control address (MAC address), which is printed on the device label, needs to be configured in the DHCP server. At the same time, the rc_visard’s host name can also be set in the Domain Name Server (DNS). Both MAC address and host name should be sent to the network administrator for configuration.
If the rc_visard cannot contact a DHCP server within about 15 seconds after startup, or after plugging in the network cable, it assigns itself a unique IP address. This process is called Link-Local. This option is especially useful for connecting the rc_visard directly to a computer. The computer must be configured for Link-Local as well. Link-Local might already be configured as a standard fallback option, as it is under Windows 10. Other operating systems such as Linux require Link-Local to be explicitly configured in their network managers.
Manual configuration¶
Specifying a persistent, i.e. static IP address manually might be useful in some cases. This address is stored on the rc_visard to be used on device startup or network reconnection. Please make sure the selected IP address, subnet mask and gateway will not cause any conflicts on the network.
Warning
The IP address must be unique within the local network and within the local network’s range of valid addresses. Furthermore, the subnet mask must match the local network; otherwise, the rc_visard may become inaccessible. This can be avoided by using automatic configuration as explained in Automatic configuration (factory default).
If this IP address cannot be assigned, e.g. because it is already used by another device in the network, IP configuration will fall back to automatic configuration via DHCP (if enabled) or a Link-Local address.